NordLink
NordLink NordLink - the "green link" for exchanging German wind energy with Norwegian hydropower - is a connection of two optimally complementary systems. NordLink is a lighthouse project and an enormously important building block of the European energy transition to compensate for dark periods and at the same time to make green energy available safely and affordably in the EU.
NordLink NordLink - the "green link" for exchanging German wind energy with Norwegian hydropower - is a connection of two optimally complementary systems. NordLink is a lighthouse project and an enormously important building block of the European energy transition to compensate for dark periods and at the same time to make green energy available safely and affordably in the EU.
- NordLink

About this project
The "green link"
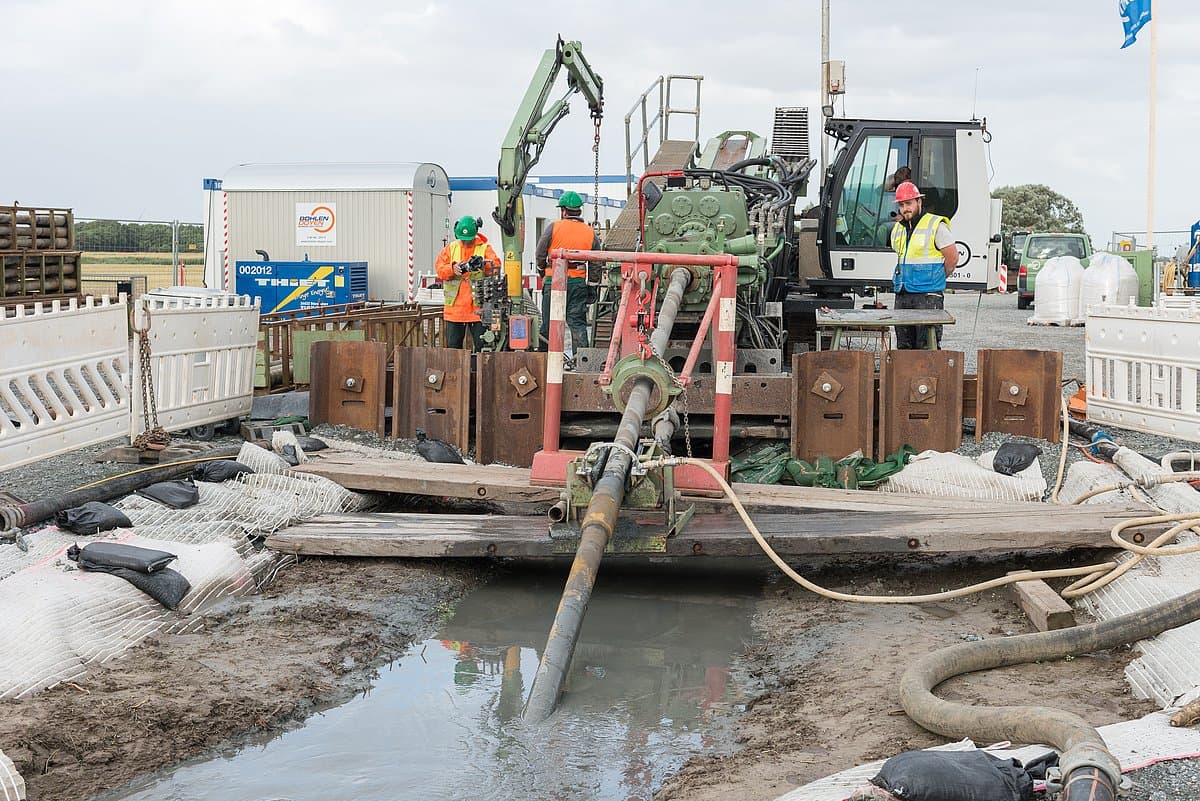
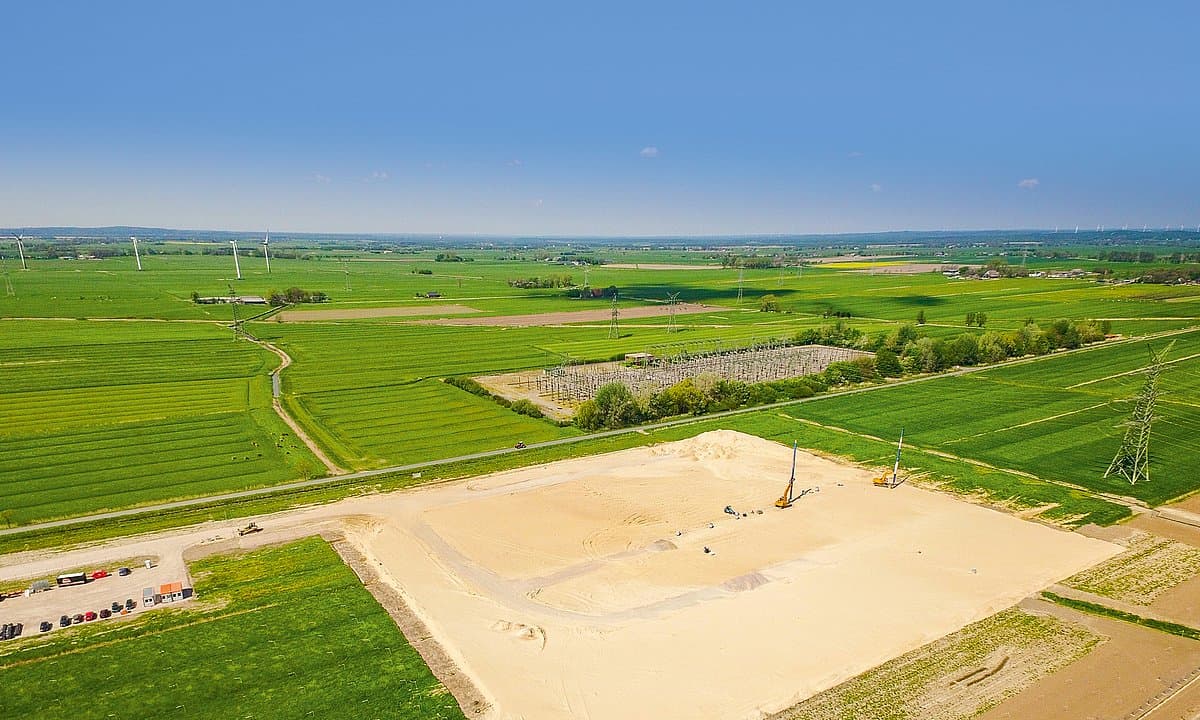
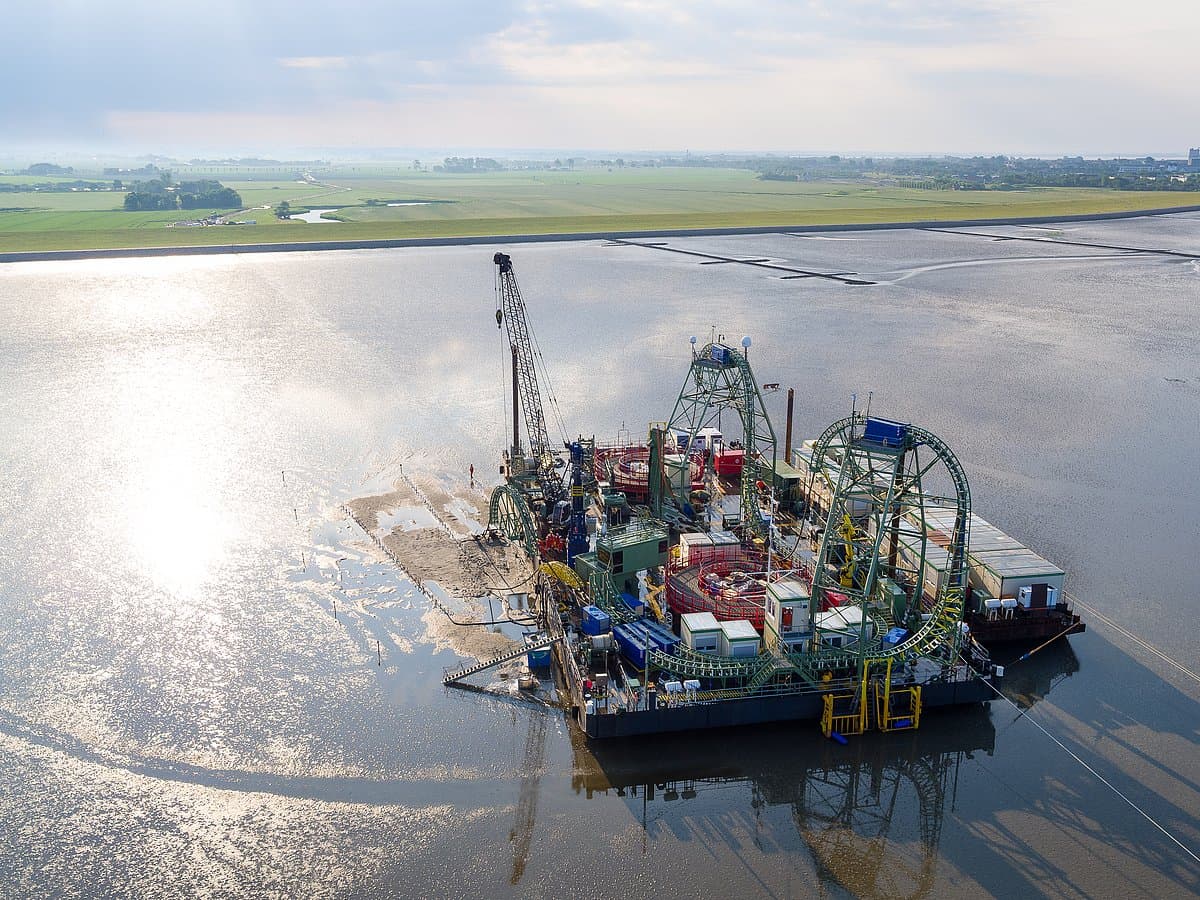
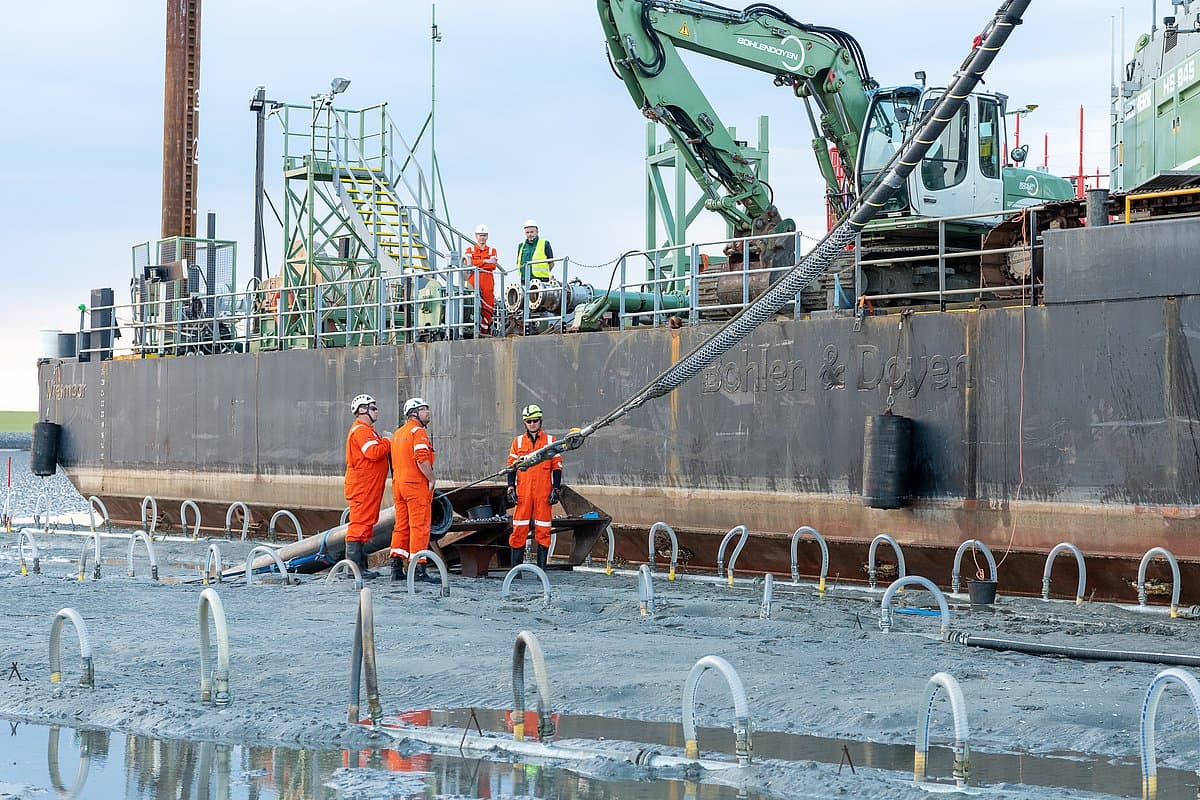
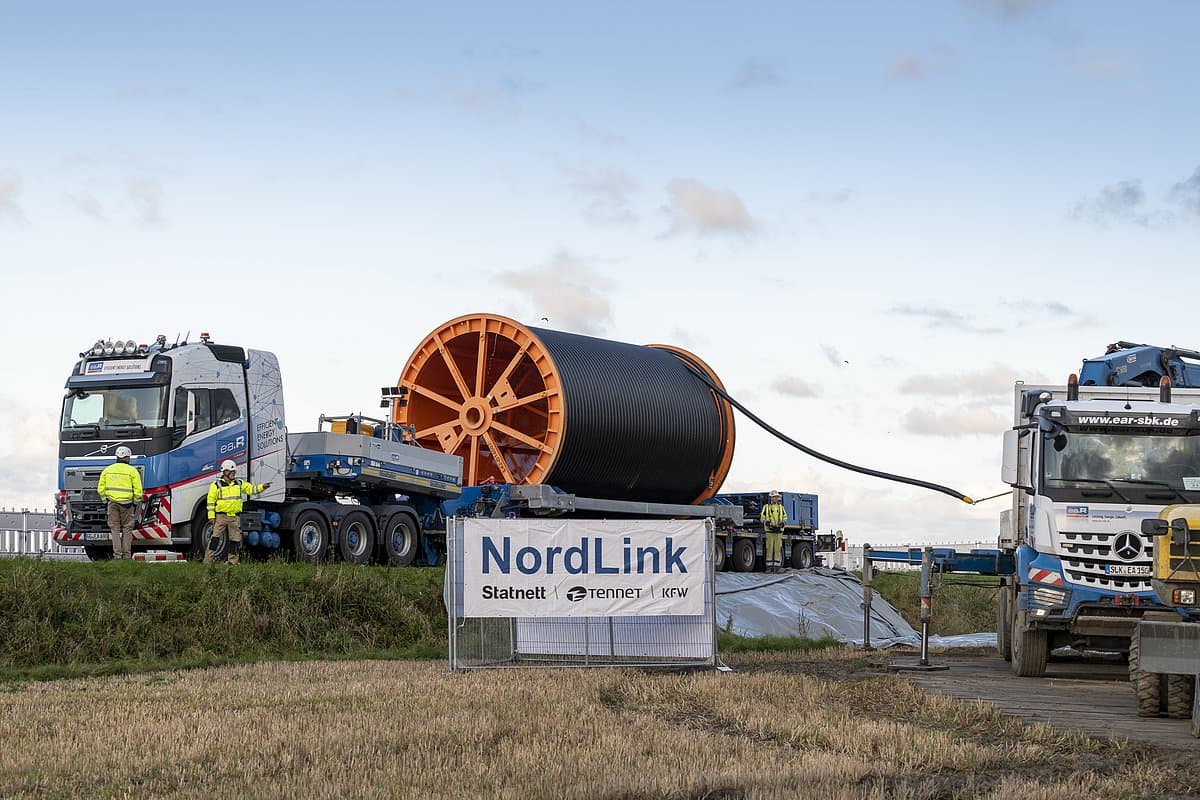
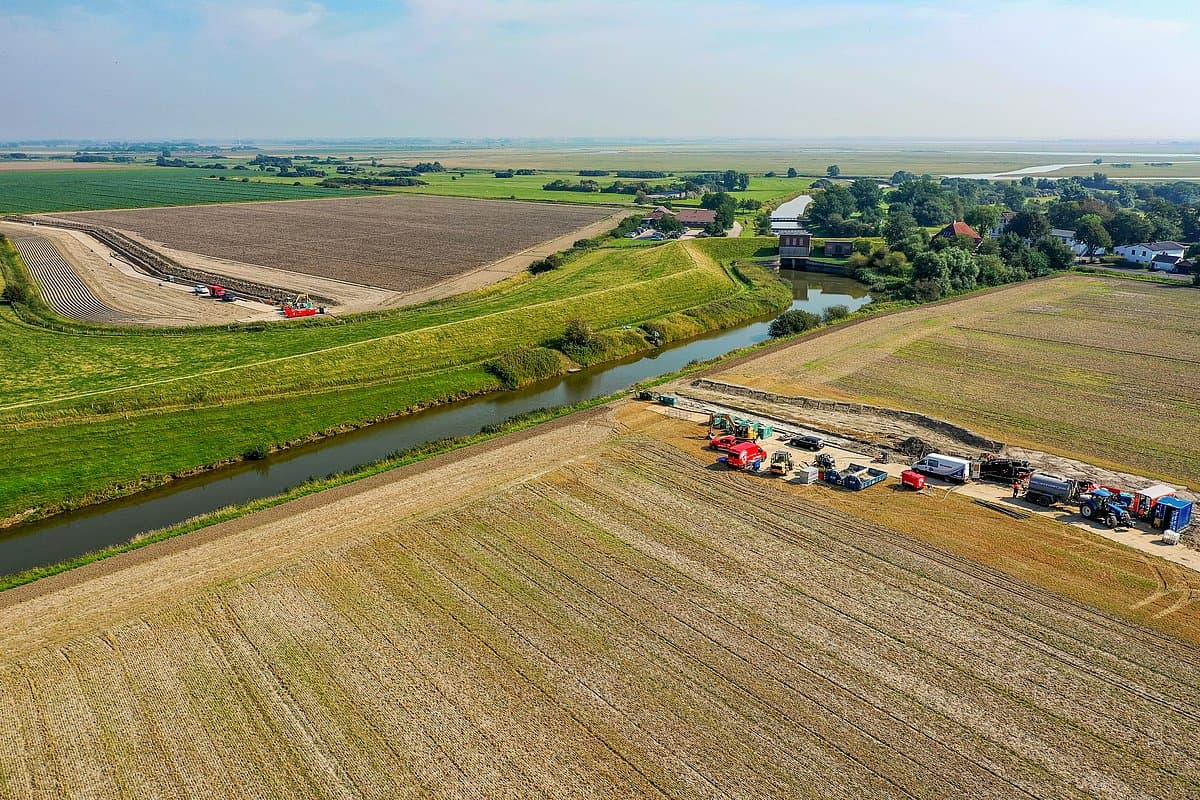
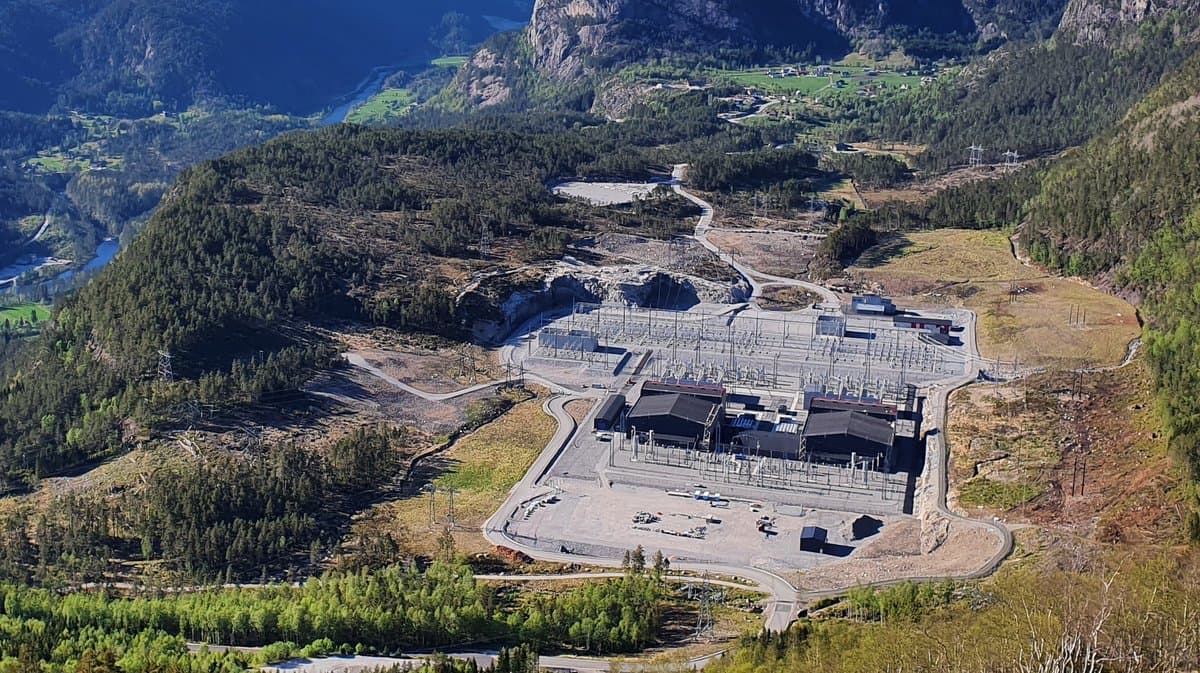
NordLink is implemented as a high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission between Germany and Norway with a route length of 623 km, whereof 516 km are realized as submarine cable. Due to its length, direct current is used to transmit the electricity through both cables (positive and negative poles), which are connected to converter stations at each end. Direct current is especially advisable over long distances and for large-scale transmissions of power.
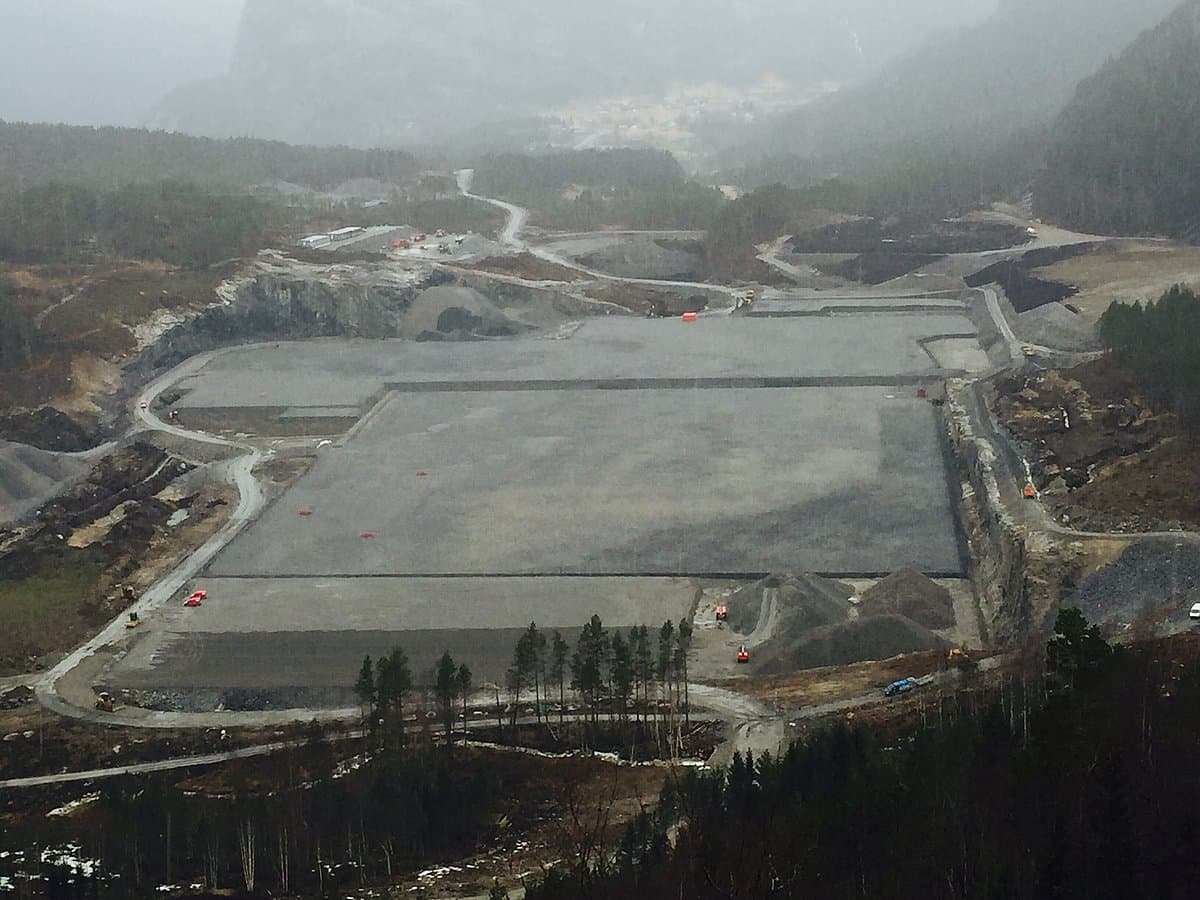
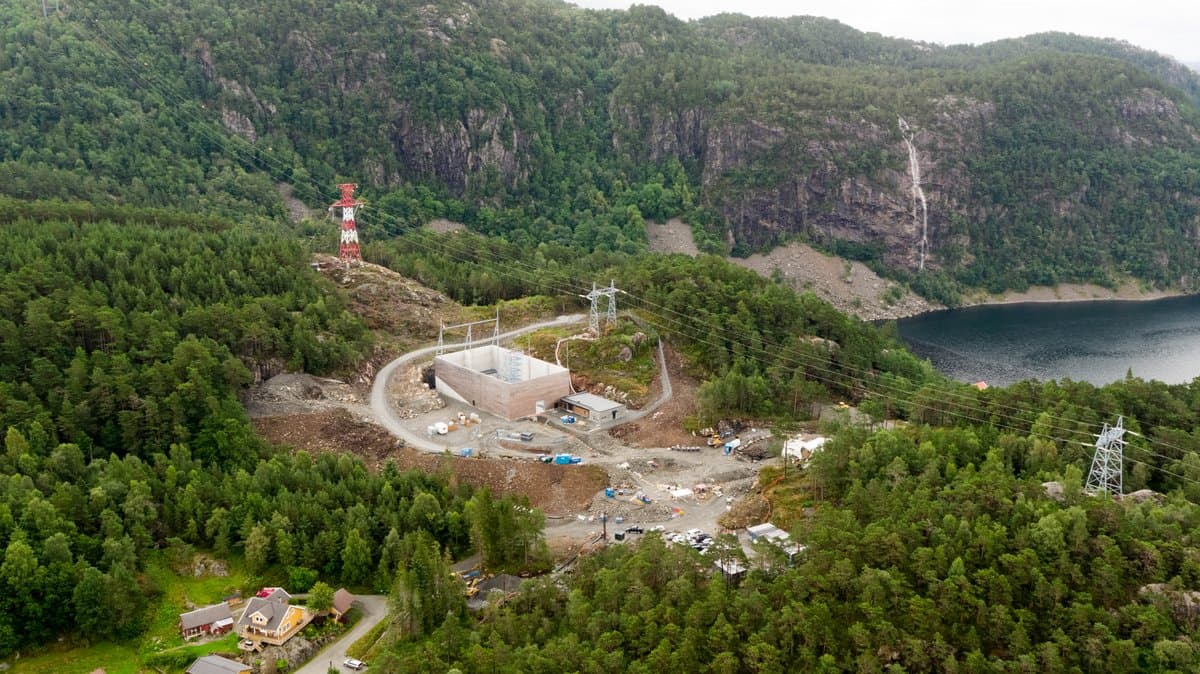
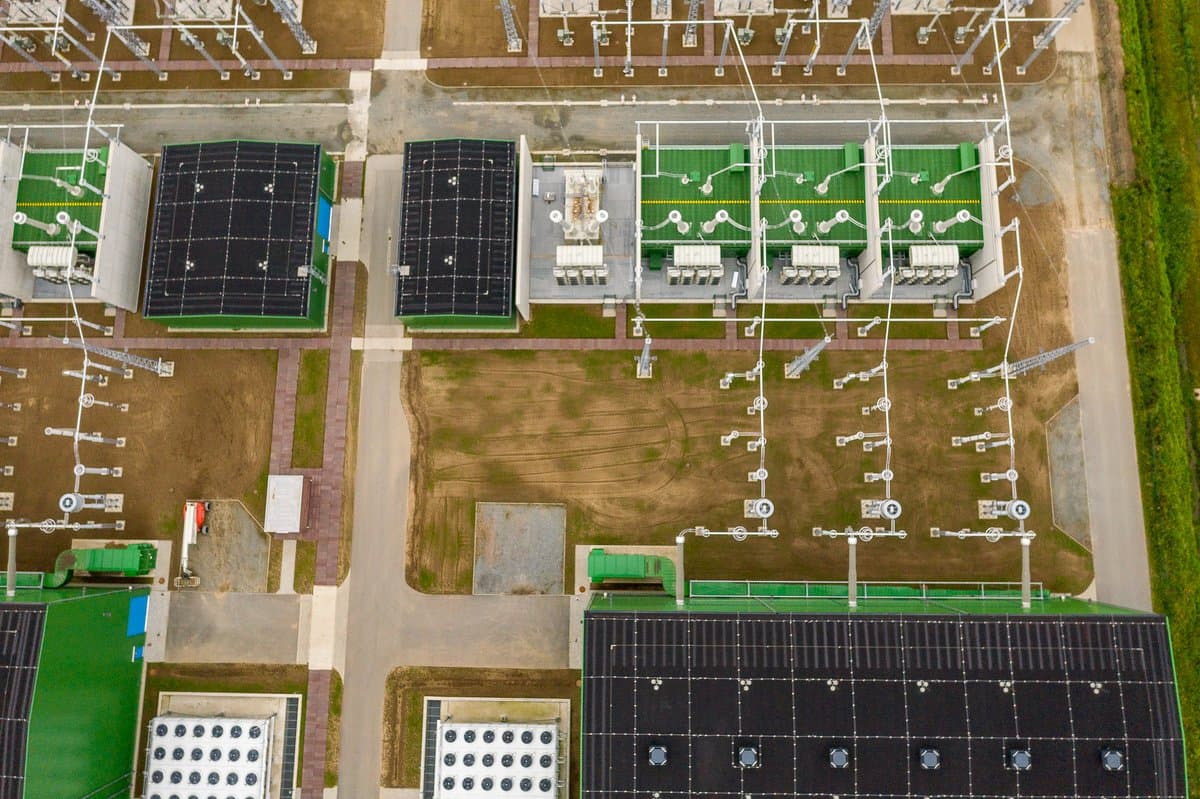
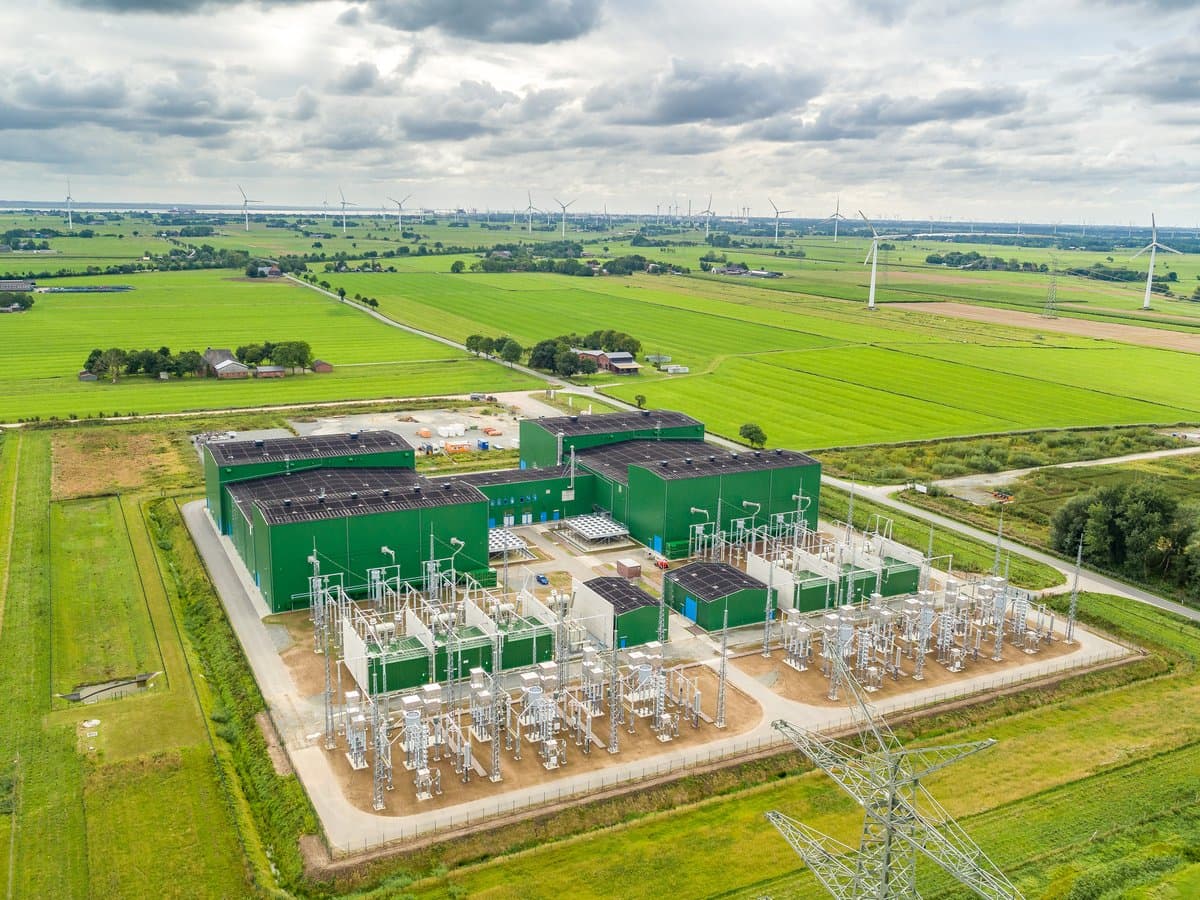
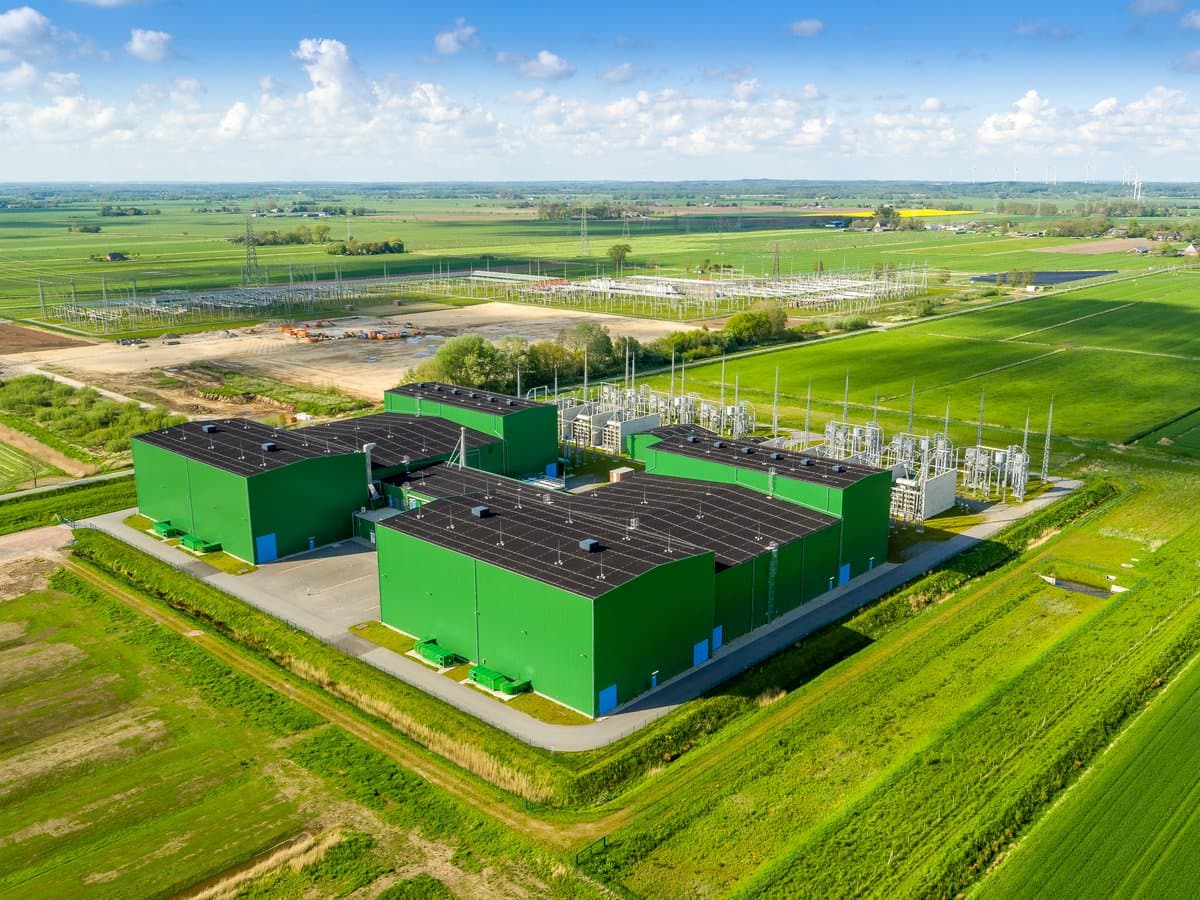
The converter stations are built in Wilster, Schleswig-Holstein/Germany, and Tonstad in Norway. At these sites, the electricity is converted from direct (DC) to alternating current (AC) - or vice versa, depending on the direction of transmission - and fed into the German or Norwegian transmission grid in order to supply households and companies with electricity. In absolute terms, NordLink can supply around 3.6 million German households.
Grid connection points
- From substation Wilster in Germany to substation Tonstadt in Norway
Figures
- 623 km
- 1.400 MW capacity at ± 525 kV DC
A driving force for the energy transition/integration of renewable energy
NordLink is a milestone in the realisation of the energy transition. With the incorporation of the project into the Federal Requirements Plan Act, the necessity and urgent need for the implementation of the project for the energy market has been established by law. The conferral of the status of ,Project of Common Interest’ by the European Union, in accordance with the new guidelines for trans-European energy infrastructure, underlines the high economic and energy-economical importance of the project at European level. NordLink – the ,green link’ – creates a connection to the capacities of hydropower plants in Norway and will counteract bottlenecks in the German transmission grid. This interconnector increases facilities for the exchange of renewable energy and plays its part in the reduction of carbon emissions and achievement of climatic objectives. NordLink has a capacity of 1,400 megawatts (MW) and can supply more than 3.6 million German households with renewable energy. This is equivalent to the same feed-in power as would be produced by 466 wind turbines at 3 MW each. This means that the capacity of the interconnector is slightly higher than that of a large conventional power station.
Impressions

European market integration
NordLink is the first interconnector to provide a direct link between the Norwegian and German energy markets. This connection promotes the integration of the North-western European energy market, increases market efficiency and contributes to a stabilisation of energy prices.
,Storage´ of wind energy
Connecting Norwegian hydropower with German wind power provides benefits for both countries. Whenever a surplus of wind energy is produced in Germany, for example, it can be transmitted via NordLink to Norway. The reservoirs in Norway then serve as natural storage for wind energy as the water remains in the reservoirs. Conversely, Germany can import hydropower from Norway when demand is high.
German-Norwegian cooperation
The NordLink project was implemented by the Norwegian TSO Statnett and DC Nordseekabel GmbH & Co. KG, each with 50% ownership. TenneT and KfW each have a 50% share in DC Nordseekabel. DC Nordseekabel was responsible for the construction and approvals on the German part of the project.
Downloads
Contacts